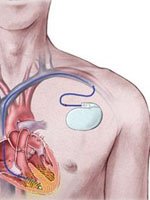
Pacemaker Implantation: A Life-Saving Procedure
A pacemaker is a small medical device implanted in the chest to regulate the heart's rhythm. It is used primarily for individuals with heart conditions that cause abnormal heart rhythms, such as bradycardia (a heart rate that is too slow) or certain types of heart block. Pacemaker implantation has become a common and effective treatment for those whose heart's natural electrical system is not functioning correctly.
What Is a Pacemaker?
A pacemaker consists of a pulse generator, which contains a battery and electronic circuits, and one or more leads (wires) that are placed in the heart. The device sends electrical impulses to the heart to prompt it to beat at a normal rate and rhythm. Pacemakers can be programmed to deliver these impulses when the heart rate falls below a preset threshold, ensuring that the heart maintains an adequate rhythm for proper blood circulation.
Why Is Pacemaker Implantation Needed?
Pacemaker implantation is typically required for patients who experience one or more of the following conditions:
- Bradycardia: A slow heart rate, usually fewer than 60 beats per minute. This can cause symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, shortness of breath, or fainting.
- Heart Block: A condition in which the electrical signals that control the heartbeat are delayed or blocked, preventing the heart from pumping effectively.
- Atrial Fibrillation with Slow Ventricular Response: A type of irregular heartbeat in which the atria beat rapidly and irregularly, leading to a slow heart rate in the ventricles.
These conditions can disrupt the heart's normal function, leading to symptoms that impair quality of life and potentially endanger health. A pacemaker helps regulate the heart's electrical activity, improving blood flow and preventing complications associated with abnormal heart rhythms.
How Is Pacemaker Implantation Performed?
Pacemaker implantation is a minimally invasive procedure that typically takes between one to two hours and is performed under local anesthesia, with the patient awake but sedated. The process involves the following steps:
Conclusion
Pacemaker implantation is a life-saving procedure that provides essential treatment for patients with heart rhythm disorders. By regulating the heart's rhythm, a pacemaker helps improve the heart's efficiency and prevents complications that could arise from abnormal heart rates. With advancements in pacemaker technology, these devices are now smaller, more efficient, and offer longer-lasting performance, enabling individuals to lead healthier, more active lives. The procedure is minimally invasive, has a low complication rate, and offers significant benefits for patients with heart conditions that affect the heart’s electrical system.